Vimeo: https://vimeo.com/309137882
YouTube: https://youtu.be/YZj6RmCgXJ8
Welcome to Kerbalism! I’m your host Aubrey Goodman. In this episode, we deploy orbital stations to our moons.
In our quest to explore our solar system, we seek new information to help us make sense of the universe, to expand our understanding of physics. Having a manned station in orbit around a moon helps pave the way toward increased traffic to the moon and acts as a support point for missions to its surface.
Just as we did for planetary stations, we first send an unmanned fuel pod into low lunar orbit. This will help prepare for future missions. Deploying a manned science station at the same altitude but on the opposite side of the orbit helps increase utility. The fuel pod acts as a last ditch option for crafts running critically low on fuel. Having both stations on the same orbit at opposite ends effectively doubles the chance a struggling craft can dock with a station.
Orbital science stations act as a staging point for science missions to the surface. We want to make sure we have docking ports of all sizes on these stations, again to maximize utility. Also, since this station will be supporting other smaller craft, it needs a large cache of fuel, monopropellant, and electricity.
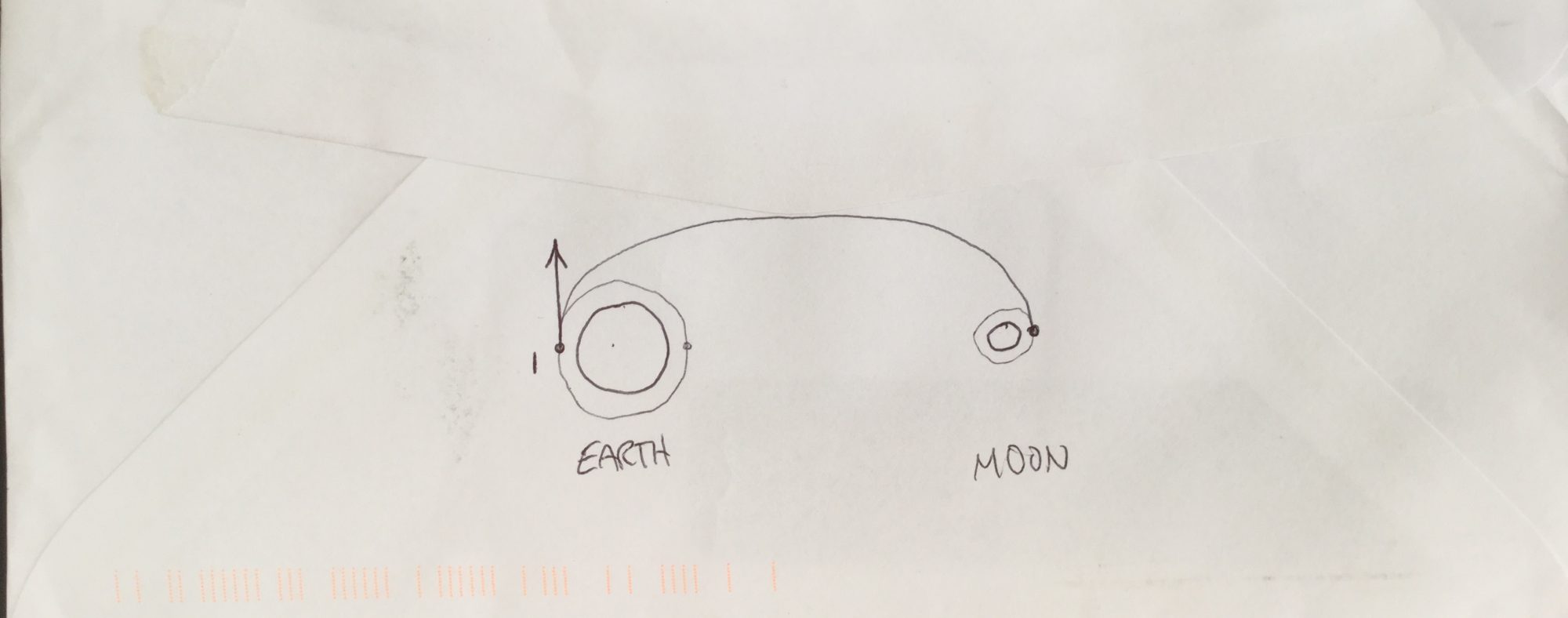
After the station is assembled in planetary orbit, with all its supporting craft docked, we’re ready for transfer orbit. With fuel reserves adequately filled, we plan and execute our lunar transfer maneuvers. This means a prograde maneuver from planetary orbit and a retrograde maneuver to settle into a low circular orbit around the moon.
From here, we can send our unmanned support craft to the surface to explore and gather samples. We can also ferry tourists to the surface for a space selfie. Tourism helps generate revenue to stoke the financial furnace to pay for our science missions.
We’ve spent a considerable amount of resources just to deploy stations to our moons. It’s going to take a lot more funding to build and deploy manned stations to other planets. In our next episode, we send a manned station to Duna, which is a lot like Mars. Don’t miss it!
And thanks for watching Kerbalism!